What are the 3 C’s of Cyber Security?
In today’s world of digital devices, no day goes by without reports about another data breach or cyber-attack. Taking a basic cybersecurity course will help you become aware of this important issue. There are three C’s of cyber security: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. They are at the heart of a good security policy. In this blog, we will explain the three pillars, why they matter, and how to keep them strong. Here, Confidentiality means protecting information against unauthorized access. The data should be accessible only to those authorized to access it. Integrity means ensuring that data is not tampered with and that the user speaks with the right server. This relates to authenticating communications. Finally, Availability is the most important pillar.
Definition and Importance of Confidentiality Cyber Security
Confidentiality means keeping sensitive information safe from unauthorized access and disclosure. To ensure privacy and trust in online transactions, there need to be strong measures to protect confidentiality. Personal details like credit card data, passwords, photos, and medical information should only be accessible to the original sender and the intended recipient. These details should not be shared with others or third parties unless the original recipient chooses to do so. Public or implied consent should not be enough to share this information.
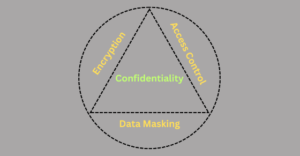
Techniques to Ensure Confidentiality
Encryption:
Encryption is the process of converting data into a remotely readable format to protect it. There are two classes of encryption: symmetric-key and asymmetric-key (also called conventional and public-key encryption). A symmetric-key algorithm uses one key for encryption and decryption, and a public-key algorithm uses a different one.
Access Controls:
Access controls authenticate a user against a record of access, such as logging in with a username and password. This includes authentication through biometrics and two-factor authentication. Authorization verifies that the user has access rights to that data or resource and is controlled with role-based access control (RBAC).
Data Masking:
Data masking is a technique used to hide specific data within a database. It allows authorized users to access and use the system without exposing sensitive information. This is especially useful in environments like testing, development, or training, where real data might be needed but should remain protected from unauthorized access. By masking the data, the system ensures that only those with proper permissions can see the actual information, while others see only masked or anonymized data.
Challenges in Maintaining Confidentiality
Even with strong security, confidentiality can still be compromised. This can happen due to insider threats, data breaches, or poor access controls. Insider threats come from employees or contractors who misuse their access. Data breaches can occur through hacking, phishing, or other cyber attacks.
Definition and Importance of Integrity in Cyber Security
Integrity ensures that data is the same from the moment it was captured (known as ‘at-rest’) and also while it’s moving or being processed (‘in-flight’) until it is finally used in a decision (otherwise known as ‘in-use’). Integrity prevents tampering with or maliciously editing data, ensuring that data never deceives.
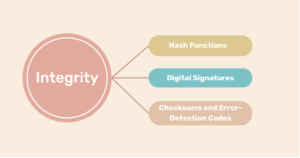
Techniques to Ensure Integrity
Hash Functions:
Hashing turns data into a fixed-length string of bytes, which acts as an identifier. A common hash algorithm is SHA-256. Hashes help ensure data integrity by comparing the hash of the original data with the hash of the received data to verify they match.
Digital Signatures:
A recipient can check the source and integrity of a digital message or document using a cryptographic system called a “digital signature“. This digital signature is a unique set of characters created by an algorithm that the sender adds to the letter. When the letter is received, the recipient can use the digital signature to verify that it hasn’t been tampered during transmission.
Checksums and Error-Detection Codes:
These simple schemes help check data integrity when sending it over a noisy wire. By adding value to your data, you can detect any changes made during transmission.
Challenges in Maintaining Integrity
Data integrity can also be affected by malware and ransomware. Malware is any code or program designed to steal data or cause damage. At the same time, ransomware demands a ransom payment to release encrypted data. Furthermore, human error can cause accidents like mistakes, unauthorized data modifications, or deletions. Also, data corruption can happen due to hardware failures, transmission errors, and other factors.
Definition and Importance of Availability in Cyber Security
We must ensure that users and service-delivery systems can always access information and resources to guarantee availability. Our infrastructures must be resilient, repairable, and socially acceptable during construction, operation, and disposal to keep businesses running.
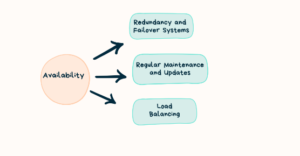
Techniques to Ensure Availability
Redundancy and Failover Systems:
We have to implement redundant systems and a failover mechanism, similar to cloud systems. If one system fails, the other takes over to prevent a service outage. Backup systems and failover strategies are crucial for maintaining high availability during unexpected outages.
Load Balancing:
Load balancing distributes incoming network traffic evenly across many servers. This avoids swamping a single server prone to high load and often improves the performance and reliability of applications and services.
Regular Maintenance and Updates:
The software needs regular updates, and the system requires tuning, maintenance, and cleaning to stay operational and minimize breakdowns. We can improve the system by adding components that increase compatibility with new systems. We also need to address security vulnerabilities through patch management.
Challenges in Maintaining Availability
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks, natural disasters, physical damage, and system failures can all thwart availability. Traffic saturation characterizes DDoS attacks, while natural disasters, physical damage, and accidents can cause infrastructure failures. Also, bugs in software or hardware systems can lead to failures.
Complete our Cyber Security Techniques Bundle course to elevate your presence.
Integration of the 3 C’s in Cyber Security Strategy
The integration of the 3 C’s cyber security strategy typically involves implementing layered defenses, encryption protocols, and robust access controls to maintain a resilient security posture against cyber threats.
Developing a Comprehensive Cyber Security Plan
Identifying risks and vulnerabilities helps uncover where a business is most threatened. This allows for better planning and prioritization to keep data secure and operations smooth. Also, balancing confidentiality and integrity with availability is crucial.
Regular Audits and Assessments
Security audits and assessments should be regularly performed to recognize weaknesses and maintain the best security posture. Security should be monitored and improved upon continuously.
Training and Awareness
Training employees in cyber threat best practices and conducting monthly sessions help enhance organizational security. These efforts empower people to understand how to respond to threats effectively.
Future Trends in Cyber Security
Future trends in cybersecurity include increased adoption of AI and machine learning for threat detection and response measures to mitigate evolving threats before they manifest into attacks.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact:
In the future, AI, machine learning, and quantum computing will drive cybersecurity degrees. These technologies will offer accessible ways to detect threats, analyze data, and meet security challenges effectively.
Evolving Threat Landscape:
Cybercriminals are becoming more skilled, so organizations must stay alert and update their security measures. Emerging threats include Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) and IoT security.
Conclusion
The 3 C’s of cyber—confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—are proven strategies for protecting information and systems. Organizations enhance their resilience by combining these strategies into a strong security program, reducing risks to critical data. To stay secure in today’s digital world, it’s essential to continually study new technologies and evolving threats.